تشدید پلاسمون سطحی و حسگرهای پلاسمونیک
تشدید پلاسمون سطحی و حسگرهای پلاسمونیک
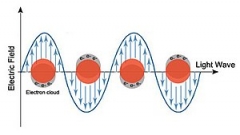
پلاسمونیک علمی است که امکان محدود کردن امواج الکترومغناطیسی در ناحیهای بسیار کوچک را فراهم کرده و به همین علت، یکی از موضوعهای جذاب در علوم مختلفی همچون پزشکی، محیطزیست و طیفسنجی است. یکی از مهمترین کاربردهای این پدیده، ساخت حسگرهای پلاسمونیک است. در پلاسمونیک، طیف بازتابی از سطح فلز یا نانوذرات فلزی به ضریب شکست محیط اطراف وابسته است و این موضوع اساس عملکرد حسگرهای پلاسمونیک است. تغییر در ضریب شکست محیط اطراف موجب تغییر طولموج، شدت و زاویه پلاسمونیک میگردد. بنابراین با پایش پیوسته این پارامترها، میتوان کمیت موردنظر را اندازهگیری کرد.
این مقاله شامل سرفصلهای زیر میباشد.
- مقدمه
- تاریخچه
- تشدید پلاسمون سطحی
- تشدید پلاسمون سطحی جایگزیده
- مقایسه حسگرهای SPR و LSPR
- بحث و نتیجهگیری
لطفا برای مشاهده متن کامل مقاله ابتدا وارد سایت شوید
منابـــع و مراجــــع
۱ - Raether, H., Surface Plasmons on SmoothRough Surfaceson Gratings. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 1988.
۲ - Maier, S.A., et al., Erratum: Plasmonics-A route to nanoscale optical devices (Advanced materials (2001) 13 (1501)). Advanced Materials, 2003. 15(7-8).
۳ - Maier, S.A., Plasmonics: fundamentalsapplications. Vol. 1. 2007: Springer.
۴ - Barnes, W.L., A. Dereux,T.W. Ebbesen, Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. nature, 2003. 424(6950): p. 824-830.
۵ - Ahmadivand, A., Plasmonic Nanoplatforms for Biochemical SensingMedical Applications. 2018.
۶ - Wood, R.W., XLII. On a remarkable case of uneven distribution of light in a diffraction grating spectrum. The London, Edinburgh,Dublin Philosophical MagazineJournal of Science, 1902. 4(21): p. 396-402.
۷ - JW, S., Dynamical theory of the grating. Proc Roy Soc A, 1907. 79: p. 399-416.
۸ - Fano, U., The theory of anomalous diffraction gratingsof quasi-stationary waves on metallic surfaces (Sommerfeld’s waves). JOSA, 1941. 31(3): p. 213-222.
۹ - Ritchie, R.H., Plasma losses by fast electrons in thin films. Physical review, 1957. 106(5): p. 874.
۱۰ - Bohm, D.D. Pines, A collective deion of electron interactions. I. Magnetic interactions. Physical Review, 1951. 82(5): p. 625.
۱۱ - Pines, D.D. Bohm, A collective deion of electron interactions: II. Collective vs individual particle aspects of the interactions. Physical Review, 1952. 85(2): p. 338.
۱۲ - Kretschmann, E.H. Raether, Radiative decay of non radiative surface plasmons excited by light. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 1968. 23(12): p. 2135-2136.
۱۳ - Kretschmann, E., Die bestimmung optischer konstanten von metallen durch anregung von oberflächenplasmaschwingungen. Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadronsnuclei, 1971. 241(4): p. 313-324.
۱۴ - Otto, A., Excitation of nonradiative surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection. Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadronsnuclei, 1968. 216(4): p. 398-410.
۱۵ - Schasfoort, R.B., Handbook of surface plasmon resonance. 2017: Royal Society of Chemistry.
۱۶ - Ahn, J.H., et al., Fiber-optic waveguide coupled surface plasmon resonance sensor. Optics Express, 2012. 20(19): p. 21729-21738.
۱۷ - Homola, J., S.S. Yee,G. Gauglitz, Surface plasmon resonance sensors. Sensorsactuators B: Chemical, 1999. 54(1-2): p. 3-15.
۱۸ - Mondal, B.S. Zeng, Recent advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance for biosensing applicationsfuture prospects. Nanophotonics in Biomedical Engineering, 2021: p. 21-48.
۱۹ - Nguyen, H.H., et al., Surface plasmon resonance: a versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors, 2015. 15(5): p. 10481-10510.
۲۰ - Hammond, J.L., et al., Localized surface plasmon resonance as a biosensing platform for developing countries. Biosensors, 2014. 4(2): p. 172-188.
۲۱ - !!! INVALID CITATION !!!
۲۲ - Schenström, K., Biofunctionalization of a Fiber Optics-Based LSPR Sensor. 2016.
۲۳ - Masson, J.-F., Portablefield-deployed surface plasmon resonanceplasmonic sensors. Analyst, 2020. 145(11): p. 3776-3800.
۲۴ - https://nicoyalife.com/nicoya-surface-plasmon-resonance-resources/what-is-spr/lspr-vs-spr-2/












حسینی
۱۴۰۳/۰۹/۲۷مدیر سیستم
۱۴۰۳/۰۹/۲۸